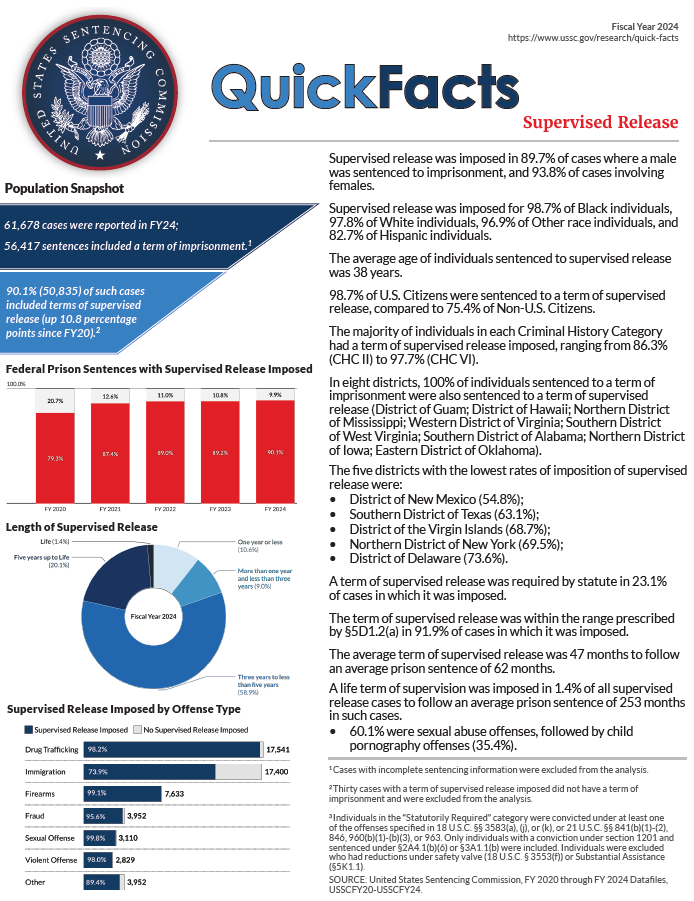
Of the 61,678 cases reported to the Commission in fiscal year 2024, 56,417 sentences included a term of imprisonment; 90.1% (50,835) of such cases included terms of supervised release (up 10.8 percentage points since fiscal year 2020).1,2
Click the cover for the PDF handout or learn more below.
IMPORTANT NOTE A guideline amendment to the supervised release policy statement is scheduled to take effect on November 1, 2025. Learn more about these upcoming changes by visiting the Amendment-In-Brief.
- Supervised release was imposed in 89.7% of cases where a male was sentenced to imprisonment, and 93.8% of cases involving females.
- Supervised release was imposed for 98.7% of Black individuals, 97.8% of White individuals, 96.9% of Other race individuals, and 82.7% of Hispanic individuals.
- The average age of individuals sentenced to supervised release was 38 years.
- 98.7% of U.S. Citizens were sentenced to a term of supervised release, compared to 75.4% of Non-U.S. Citizens.
- The majority of individuals in each Criminal History Category had a term of supervised release imposed, ranging from 86.3% (CHC II) to 97.7% (CHC VI).
- In eight districts, 100% of individuals sentenced to a term of imprisonment were also sentenced to a term of supervised release (District of Guam; District of Hawaii; Northern District of Mississippi; Western District of Virginia; Southern District of West Virginia; Southern District of Alabama; Northern District of Iowa; Eastern District of Oklahoma).
- The five districts with the lowest rates of imposition of supervised release were:
- District of New Mexico (54.8%);
- Southern District of Texas (63.1%);
- District of the Virgin Islands (68.7%);
- Northern District of New York (69.5%);
- District of Delaware (73.6%).
- A term of supervised release was required by statute in 23.1% of cases in which it was imposed.
- The term of supervised release was within the range prescribed by §5D1.2(a) in 91.9% of cases in which it was imposed.
- The average term of supervised release was 47 months to follow an average prison sentence of 62 months.
- A life term of supervision was imposed in 1.4% of all supervised release cases to follow an average prison sentence of 253 months in such cases.
- 60.1% were sexual abuse offenses, followed by child pornography offenses (35.4%).
1 Cases with incomplete sentencing information were excluded from the analysis.
2 Thirty cases with a term of supervised release imposed did not have a term of imprisonment and were excluded from the analysis.
3 Individuals in the “Statutorily Required” category were convicted under at least one of the offenses specified in 18 U.S.C. §§ 3583(a), (j), or (k), or 21 U.S.C. §§ 841(b)(1)-(2), 846, 960(b)(1)-(b)(3), or 963. Only individuals with a conviction under section 1201 and sentenced under §2A4.1(b)(6) or §3A1.1(b) were included. Individuals were excluded who had reductions under safety valve (18 U.S.C. § 3553(f)) or Substantial Assistance (§5K1.1).
SOURCE: United States Sentencing Commission, FY 2020 through FY 2024 Datafiles, USSCFY20-USSCFY24.
Data from the Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts
Of the 121,777 individuals under post-conviction supervision in the federal system:
- 89.7% were serving terms of supervised release, 9.8% were serving probation, 0.4% parole, and 0.2% remained under BOP custody.4
- The majority of individuals under post-conviction supervision in each circuit were serving terms of supervised release, ranging from 87.6% (4th Circuit) to 91.4% (7th Circuit).
- 41.2% were convicted of a drug offense, followed by firearms (18.2%) and property offenses (13.6%).5
- 89.7% were serving terms of supervised release, 9.8% were serving probation, 0.4% parole, and 0.2% remained under BOP custody.4
- Of the 51,576 supervision cases closed during the year:6
- 66.1% closed without revocations;
- 18.1% closed due to early termination.
- 33.9% closed with revocations;
- 23.1% closed due to a technical violation.
- 66.1% closed without revocations;
4 AO Data Table E-2 Federal Probation System – Persons Under Post-Conviction as of September 30, 2024. Probation includes conditional release, probation, and the former categories known as judge probation and magistrate judge probation. Parole includes parole, special parole, mandatory release, and military parole. BOP custody accounts for Bureau of Prisons Federal Location Monitoring and Elderly Home Confinement (effective Jan 26, 2020).
5 AO Data Table E-3 Federal Probation System – Persons Under Post-Conviction Supervision, by Offense as of September 30, 2024. Drugs includes data reported for previous periods as drug laws. Firearms includes data reported for previous periods as weapons and firearms. Property includes data reported for previous periods as burglary, larceny, embezzlement, fraud, auto theft, forgery and counterfeiting, and postal laws. Violence includes data reported for previous periods as homicide, robbery, and assault. Public order includes data reported for previous periods as general offenses, traffic, and Other includes nonpayment and other (federal statutes).
6 AO Data Table E-7A Federal Probation System – Post-Conviction Supervision Cases Closed With and Without Revocation by Type, During the 12-Month Period Ending September 30, 2024. A case is closed upon revocation when a judge, parole commission, or other judicial authority finds the defendant violated one or more of conditions imposed as part of the supervision term and that termination of the supervision term is warranted pursuant to applicable federal statutes, U.S. Sentencing Commission Policy Statements, the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure, and various other administrative rules. Resentencing upon revocation may, but does not necessarily, result in a term of imprisonment. Major includes involvement in or conviction of a new major offense, including absconded from custody, arrested, or another charge or convicted and sentenced to more than 90 days imprisonment, or more than one year probation. Minor includes conviction for minor offenses such as drunk driving, disorderly conduct, petty theft, traffic violation, etc. when sentence is 90 days or less imprisonment, or one year or less probation or fine. Technical includes revocation of the conditions of post-conviction supervision for reasons other than conviction for a new offense. Other closure without revocation excludes cases that were transferred out and cases closed due to death.